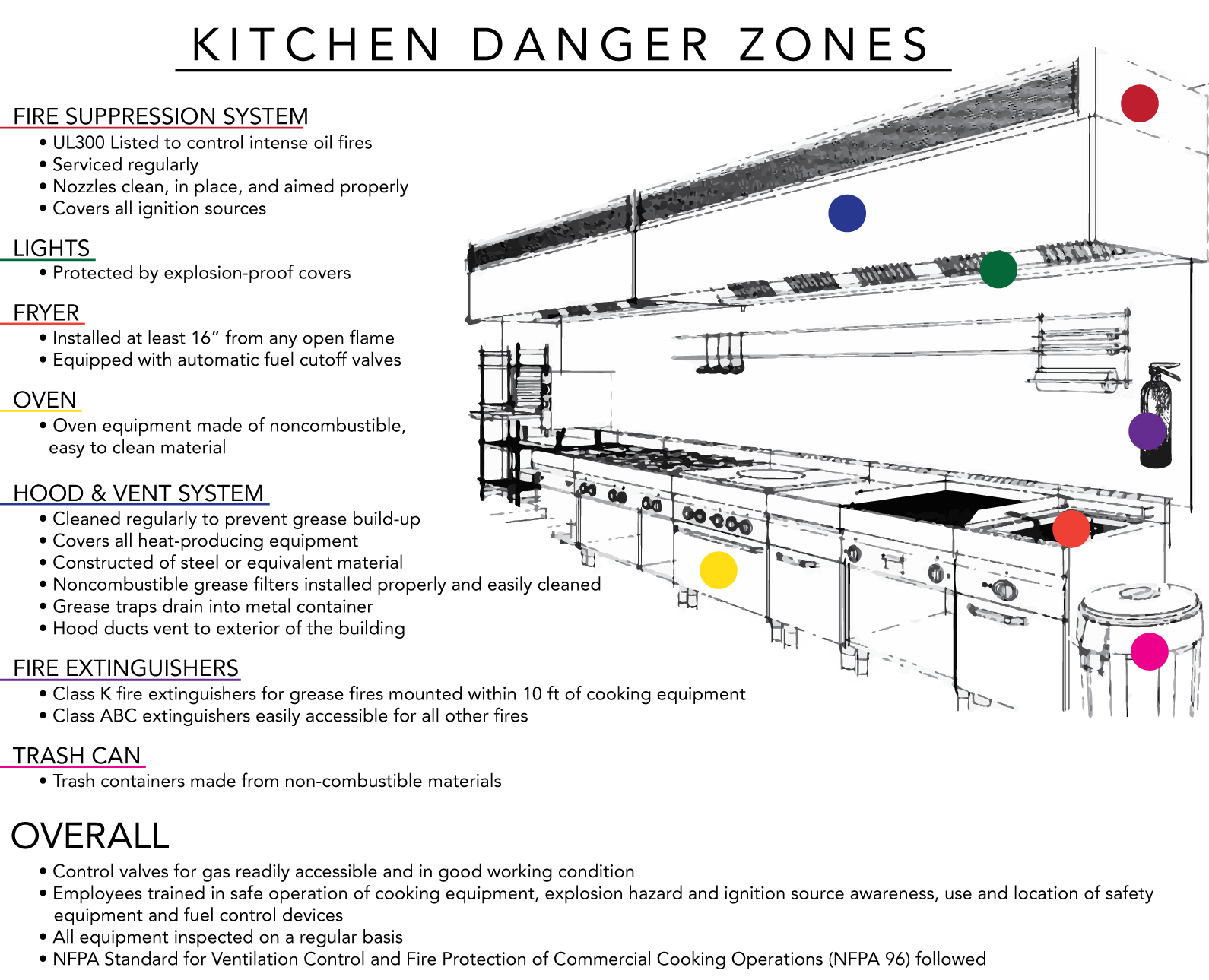
Installed Extinguishing Systems Powerpoint Presentation

Designed for employee safety training - covers essential information for employee safety training. Fully customizable for specific workplace environments. Use these Safety PowerPoints in conjunction with other safety training material in the safety library. Activation Windows Is Already Activated on this page. Audio Video Sync Test Video. Training Requirements For OSHA General Industry Standards?
Employee Emergency Plans and Fire Prevention Plans (1910.38) (a.5.i) Designate and train a sufficient number of persons to assist in emergency evacuation of employees. (a.5.ii) Review the plan with covered employees: (A) when the plan is developed; (B) whenever the employee's responsibilities change; and (C) whenever the plan is changed.(a.5.iii) Review with employees upon initial assignment parts of the plan employees must know in the event of an emergency. The written plan must be kept at the workplace and made available to employees.
NFPA 13-Installation of Sprinkler Systems. 4.10 Testing of Fixed Extinguishing Systems. Minimal design & installation of systems. Fire Detection and Suppression Chapter 6 Sprinkler Systems Effectiveness of Sprinkler Systems 96 percent reliable when installed and maintained properly Insurance.
Employers with ten or fewer employees may communicate the plan orally. (b.4.i) Apprise employees of the fire hazards to which they are exposed. (b.4.ii) See (a.5.iii). Powered Platforms for Building Maintenance (1910.66) (i.1.i) Only persons proficient in operation of a particular platform can operate a working platform. (i.1.ii.) Employees operating working platforms must be trained in recognizing and preventing safety hazards, and knowing emergency action plans, work procedures and how to take care of personal fall arrest systems. (i.1.iii) A competent person must perform training.
(i.1.iv) Provide written work procedures for employee training. (i.1.v) Certify employee training. Ventilation (1910.94) (d.9.i) Employees working in and around open surface tanks must be instructed about hazards in their jobs.
(d.9.vi) Train employees using respirators in an emergency. (d.11.v) A trained standby must be present when someone enters a tank containing a hazardous atmosphere. Occupational Noise Exposure (1910.95) (i.4) Provide training in the use and care of all hearing protectors. (k.1) Institute a training program for all employees exposed to noise at or above an eight-hour time-weighted average (TWA) of 85 decibels (dB), and ensure that every em-ployee participates. (k.2) Repeat training program annually for employees included in the hearing conservation program. Update information in the program to keep it consistent.
(k.3) Ensure employees are informed of the following: (i) effects of noise on hearing; (ii) purpose of hearing protectors, the advantages, disadvantages and attenuation of various types, and instruction on selection, fitting, use and care; and (iii) purpose of audiometric testing, and an explanation of the test procedures. Flammable & Combustible Liquids (1910.106) (b.5.vi.V.2) Post detailed flood emergency instructions. (b.5.vi.V.3) Inform station operators who carry out flood instructions of valve location.
Explosives & Blasting Agents (1910.109) (d.3.i) Drivers of explosives carriers must be familiar with traffic regulations. (d.3.iii) Attendants to drivers must be aware of materials in the truck and what measures to take to protect the public from dangers. (g.3.iii.A) Operators of bulk delivery vehicles carrying blasting agents must be trained in safe operations of the vehicle and the material being delivered. (g.6.ii) Drivers of vehicles carrying packaged blasting agents must be familiar with vehicle and traffic laws. (h.4.ii.B) Operators of water gel bulk delivery and mixing vehicles must be trained in safe operations of the vehicle and its related equipment. Storage and Handling of Liquified Petroleum Gases (1910.110) (b.16) Train personnel performing installation, removal, operation and maintenance work.
Storage & Handling of Anhydrous Ammonia (1910.111) (b.13.ii) Instruct personnel unloading tank cars. Process Safety Management of Highly Hazardous Chemicals (1910.119) (g.1) Initially train all employees involved in a process and newly assigned to a process as specified in paragraph (f) of the standard. (g.2) Provide refresher training at least every three years, and more often if necessary, for all employees operating a process. (g.3) Document training kept and include the identity of the employee, the date of training and the means used to verify that the employee understood the training.